Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeThe odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol
Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com
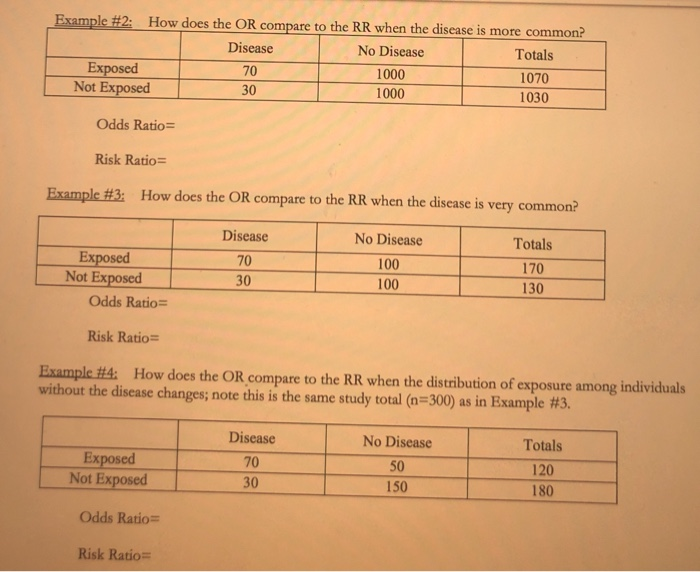
Odds vs risk ratio
Odds vs risk ratio-A risk ratio is a good measure to use for a metaanalysis if you have data from longitudinal cohorts or clinical trials It is generally thought to be easier to interpret than an odds ratio Risk Ratio is often expressed as a factor and a whole positive number, such as " is times more likely" The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the
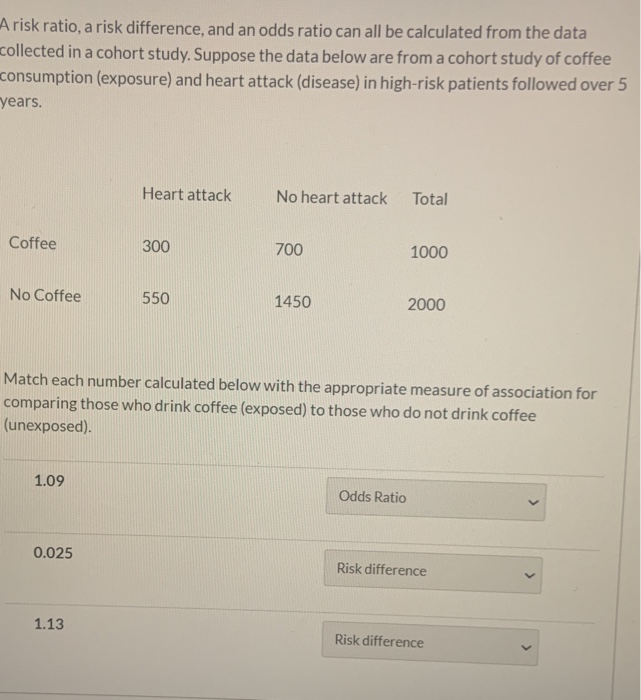



A Risk Ratio A Risk Difference And An Odds Ratio Chegg Com
Week 6 Proportions, risk ratios and odds ratios Risk ratio or relative risk Chisquared tests are tests of significance, they do not provide estimates of the strength of relationships There are different ways of doing this for different kinds of data and sizes of table, but two are particularly important in health research the risk ratio orThe odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio?When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the
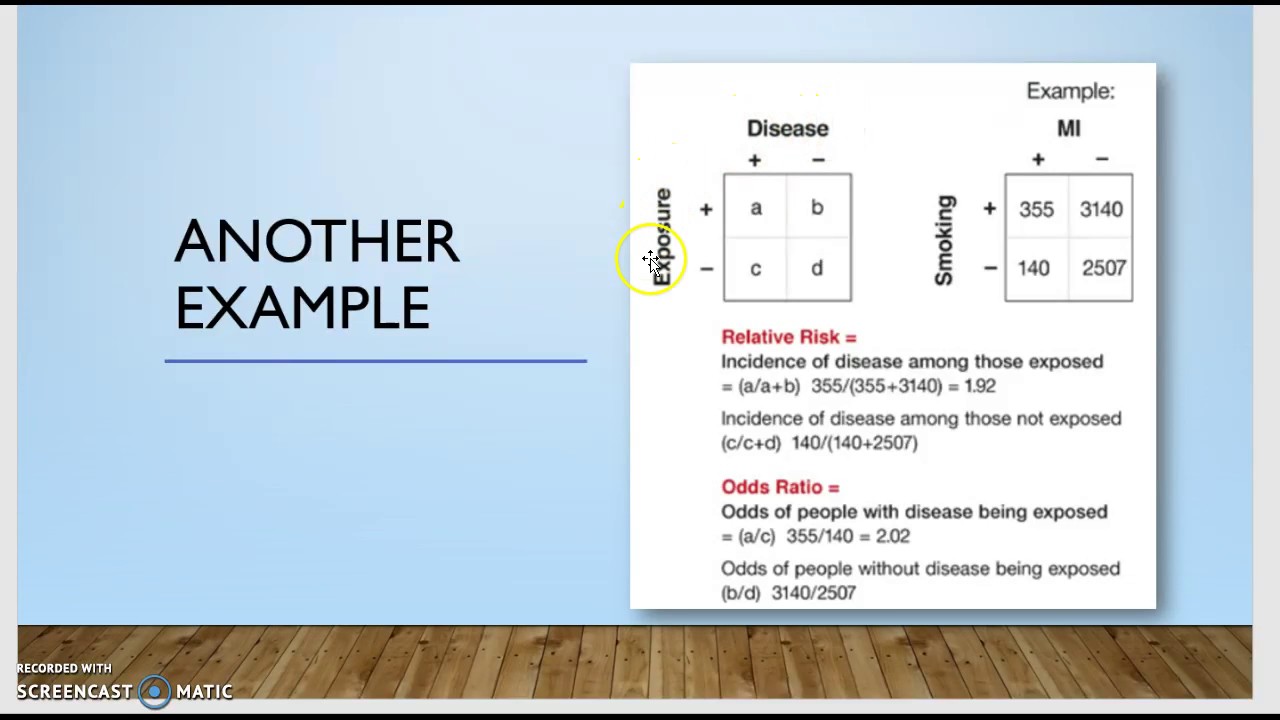
The odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and theThe relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks is Odds Ratio The OR is a way to present the strength of association between risk factors/exposures and outcomes If the OR is 1 means the odds are increased for a given outcome Let's
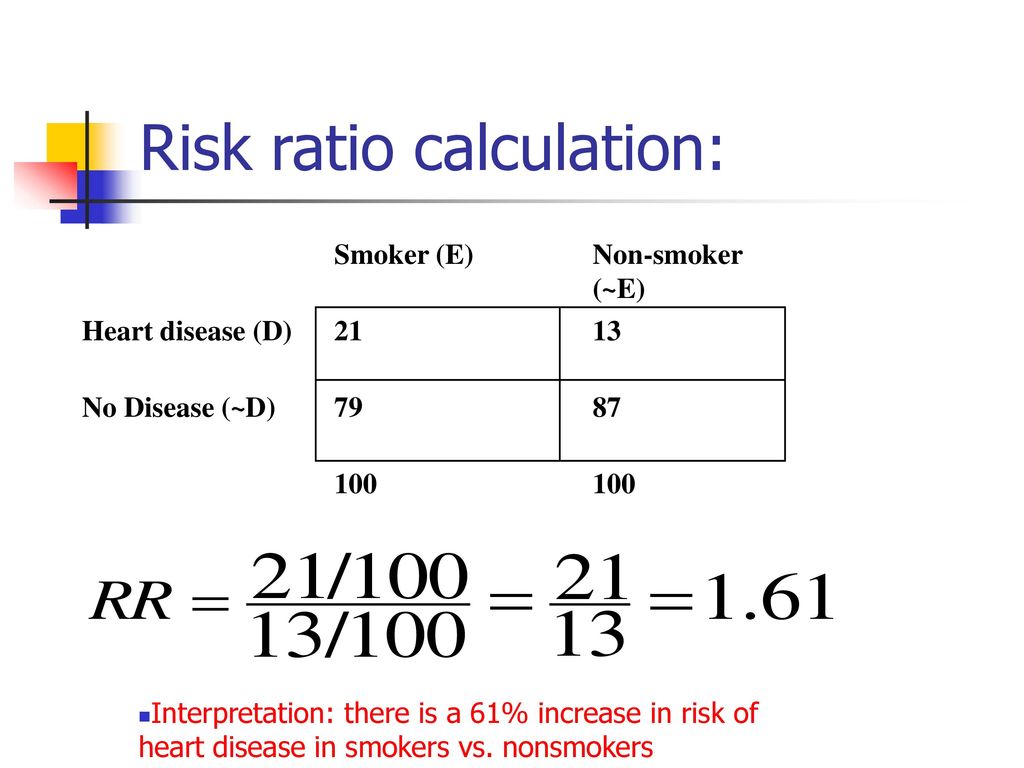
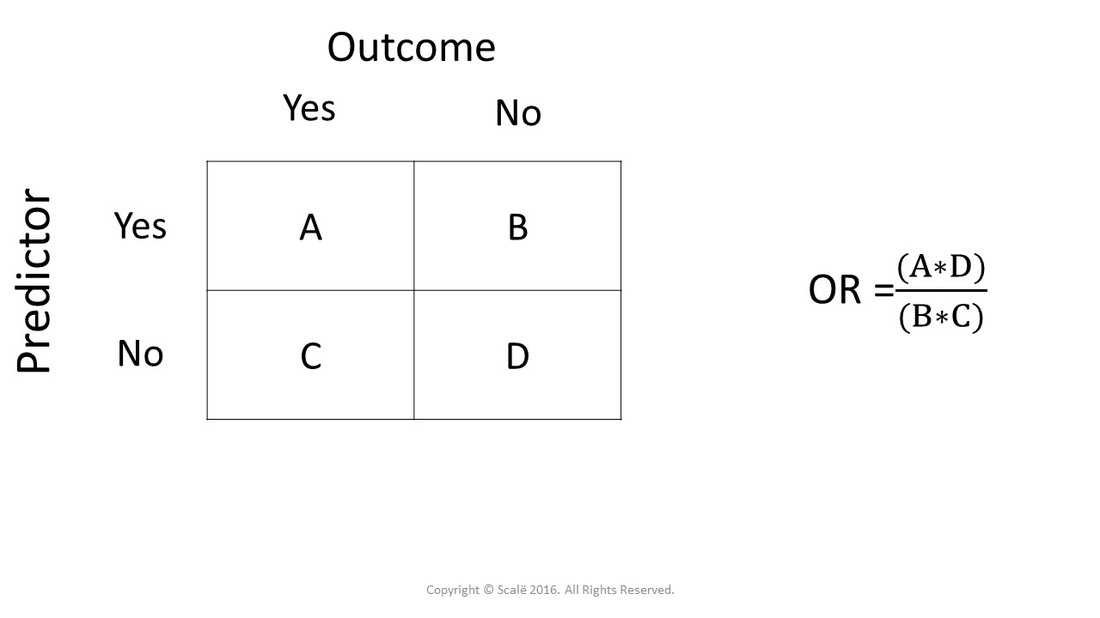
Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in a treatment group to the probability of an event occurring in a control group It is calculated as Relative risk = A/ (AB) / C/ (CD) In short, here's the difference An odds ratio is a ratio of two odds A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceThe risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisons by dividing the risk for one group (usually the group exposed to the risk factor) by the risk for the second, nonexposed, group This gives us the risk ratio



The Binomial Applied Absolute And Relative Risks Chi Square Ppt Download




Risk Ratio Of The Decrease 30 And Odds Ratio Of The Increase 40 Download Scientific Diagram
3) The Odds Ratio 4) After calculating the odds ratio, we observe a 3fold difference in the prevalence rate (75% vs 25%) change to a 9fold difference in the odds ratio Clearly, the two methods produce opposing results Effect of Changing Incidence on OR Problem Let us consider the relationship between smoking and lung cancerThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studiesIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratios



Odds Ratio




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability We can define the following terms The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokersOdds ratio and relative risk




Mixing Of Confounding And Non Collapsibility A Notable Deficiency Of The Odds Ratio American Journal Of Cardiology




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc
That is one of the attractive features of the odds ratio — when the health outcome is uncommon, the odds ratio provides a reasonable approximation of the risk ratio Another attractive feature is that the odds ratio can be calculated with data from a casecontrol study, whereas neither a risk ratio nor a rate ratio can be calculatedA comparison of odds, the odds ratio, might then make sense OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987)Since all of the measures are ratios, either of probabilities or of odds, it is clearer and simpler to use the word ratio in describing each type Risk reflects the proportion of persons experiencing the event, so it follows that comparing two cumulative incidences is called a risk ratio Relative Rate




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Understanding Measures Of Association Or Risk Odds Ratio Communitymedicine4all
This is called the odds ratio; Risk ratio = ratio of 2 cumulative incidence estimates = relative risk; If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsIn clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated
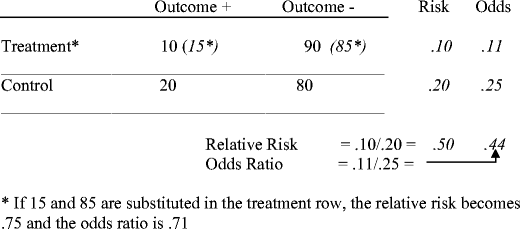



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink




A Risk Ratio A Risk Difference And An Odds Ratio Chegg Com
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents




Literature Search



Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Categorical Data And Chi Square Tests Biostatistics For The Health Sciences
The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event or disease occurring in one group to the odds occurring in another group The standard formula is X / ( 1 − X) / Y / ( 1 − Y), where X and Y are the probability of that event in the two groups, respectively In contrast, the relative risk is the risk of an event or disease"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the twoOdds ratio is often used to refer to the ideal ratio of the chances of an event happening in one group vs the chances of it happening in another This is important as an example could include outlining the probability of various individuals getting infected and dividing it with the probability of another group failing to get infected




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
In health care it is the ratio of the number of people with the event to the number without It is commonly expressed as a ratio of two integers For example, an odds of 001 is often written as 1100, odds of 033 as 13, and odds of 3 as 31The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal Plot showing the relationship between risk ratio and odds ratio for various baseline risks with y=x in blue for comparison Captions Summary Description English Plot showing the relationship between risk ratio and odds ratio for various baseline risks with y=x in blue for comparison Date 21 February 21 Source




Forest Plot Showing Relative Statistics Of Odds Ratio A And B Or Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (TheIn gambling, the odds describes the ratio of the size of the potential winnings to the gambling stake;In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratios To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrenceAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinity then the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of odds, where the odds in each group is computed as follows OR = (a/b) / (c/d) As with a risk ratio, the convention is to place the odds in the unexposed group in the denominatorMore on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream
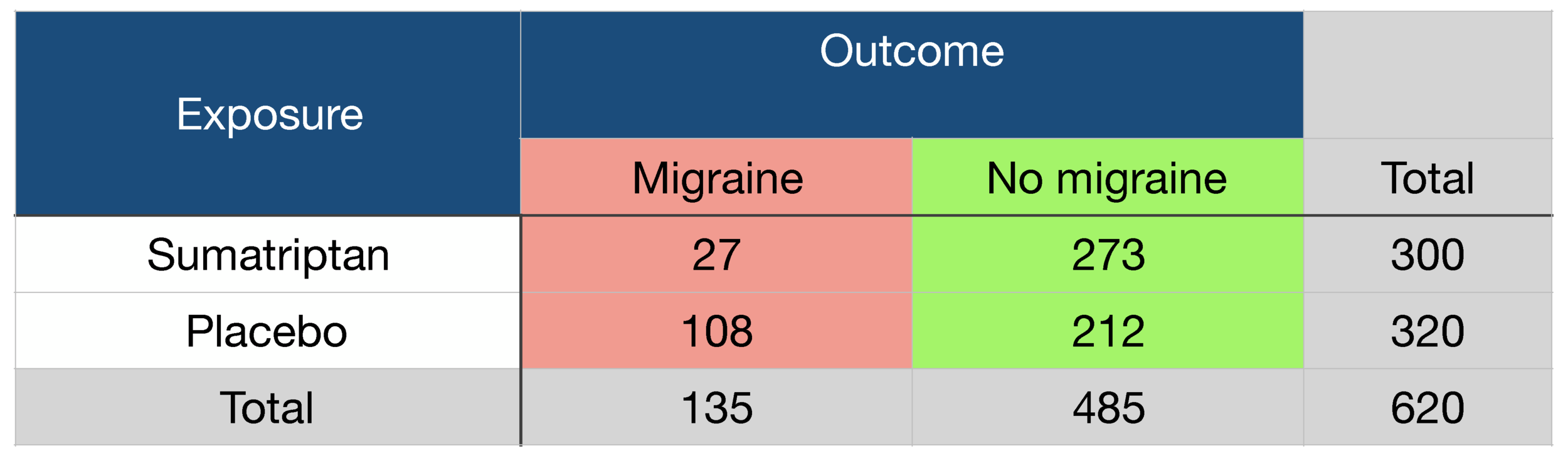
A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group Percent Relative Effect An alternative way to look at and interpret these comparisons would be to compute the percent relative effect (the percent change in the exposed group) In essence, we regardAn odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratioThe relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group




Hazard Ratio Odds Ratio




7 Stats Ideas Research Methods Statistics Math Nursing Research




Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar




Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Difference Between Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio Understanding Clinical Data Analysis Learning Statistical Principles From Published Clinical Resear




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key
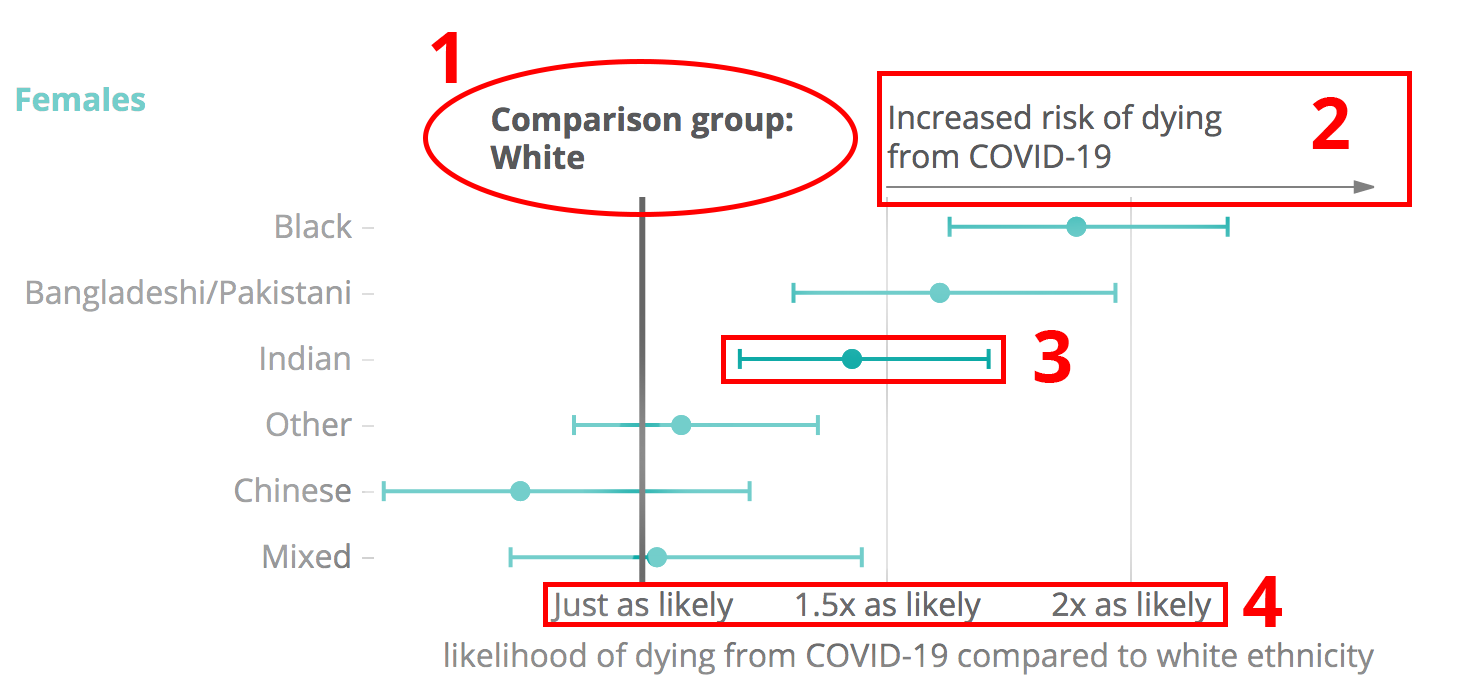



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Pocket Dentistry




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




What Are Cross Tables Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Gcp Service




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
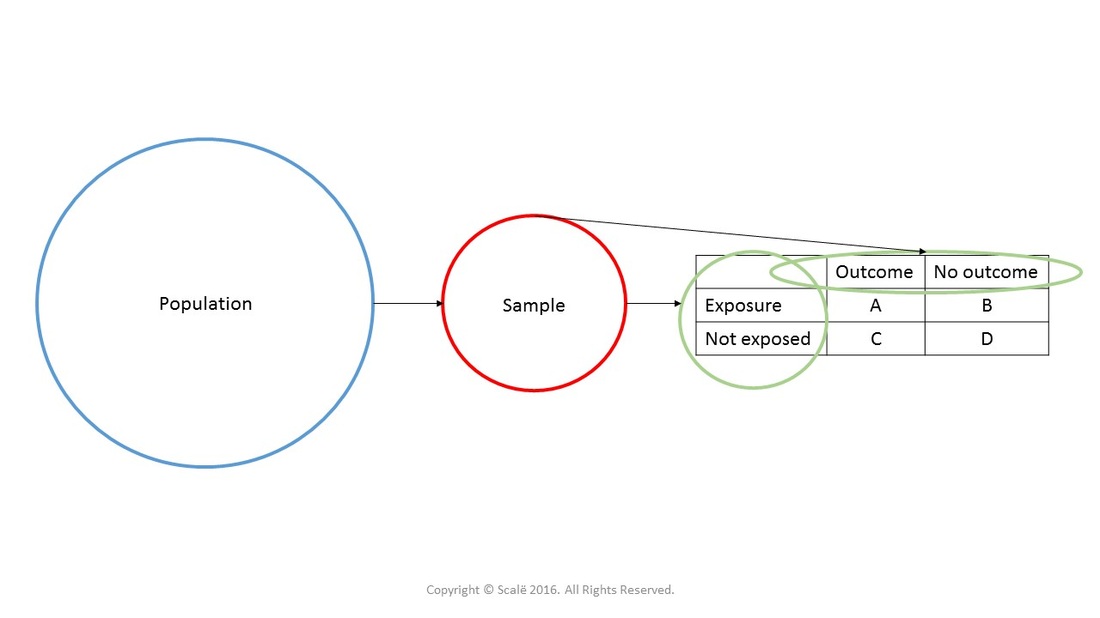



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08
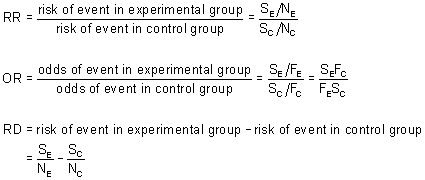



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
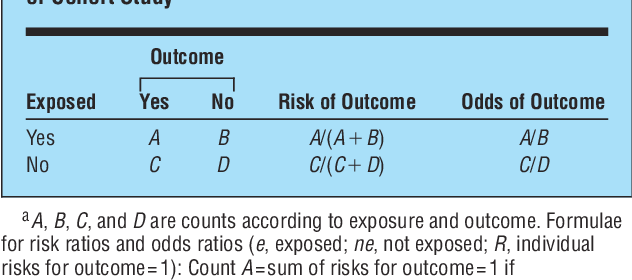



Pdf The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar



Attributable




Glossary Of Research Terminology




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Sensitivity Analysis To Compare The Use Of Risk Ratio Rr With Odds Download Scientific Diagram




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube




Statistics For Clinicians Biostatistics Course By Kevin E




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Incidence Download Scientific Diagram




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Forest Plot Of Relative Risks Or Odds Ratios From Eighteen Download Scientific Diagram




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Article




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



1




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Calculating Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Rate Ratio Youtube




Risk Difference Rd Risk Ratio Rr And Odds Ratio Or For The Download Table




Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio
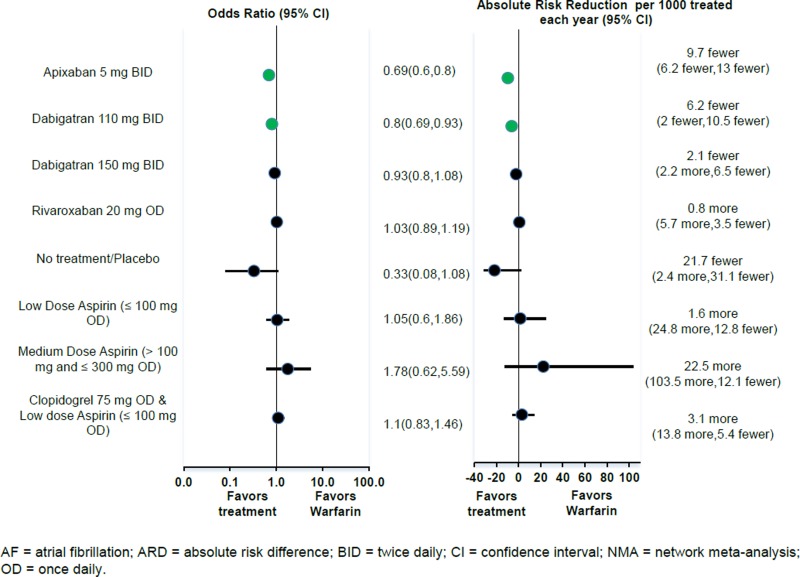



Figure 3 Odds Ratio And Absolute Risk Difference Of Major Bleeding For Antithrombotic Therapies Relative To Adjusted Dose Warfarin For Patients With Af Fixed Effects Nma Antithrombotic Agents For The Prevention Of Stroke



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Number Needed To Treat




Odds Vs Risk Ratio ただの悪魔の画像



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram
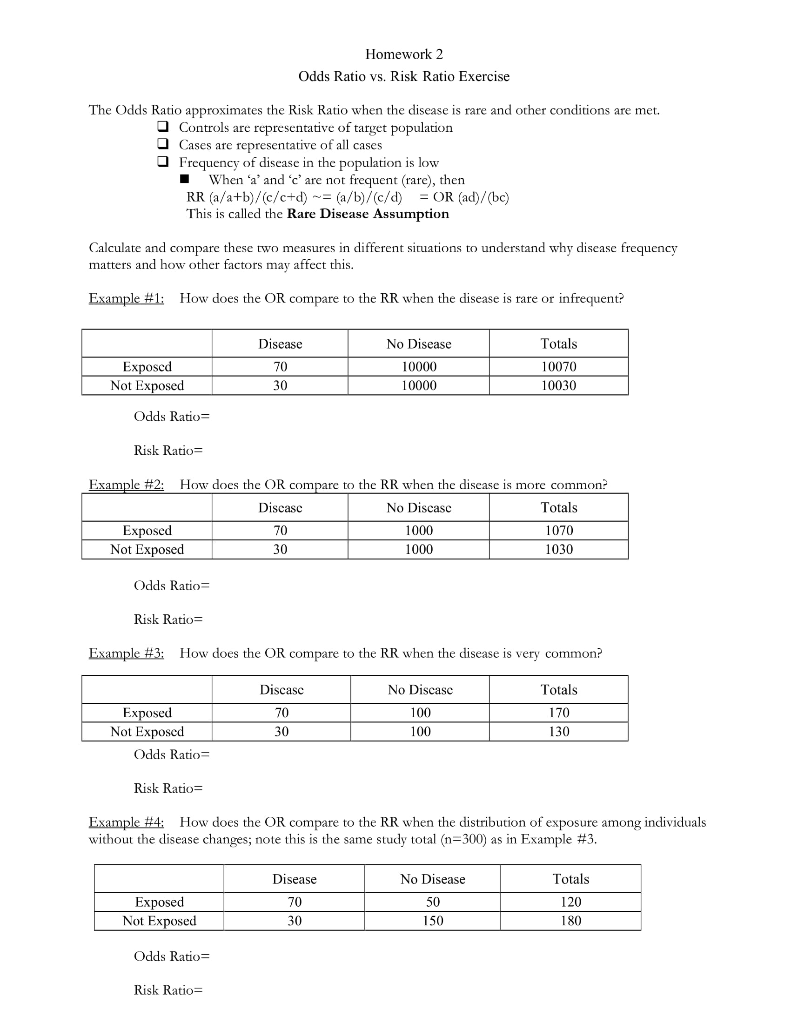



Homework 2 Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Chegg Com
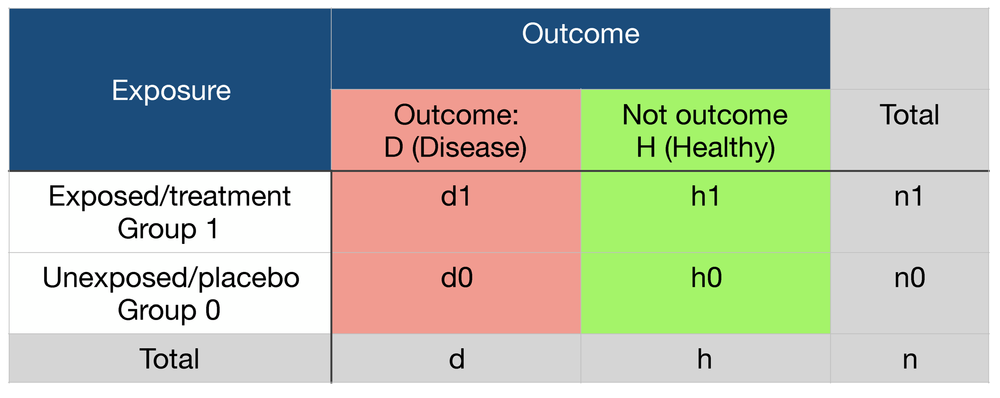



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gpraj




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio For Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Download Scientific Diagram




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
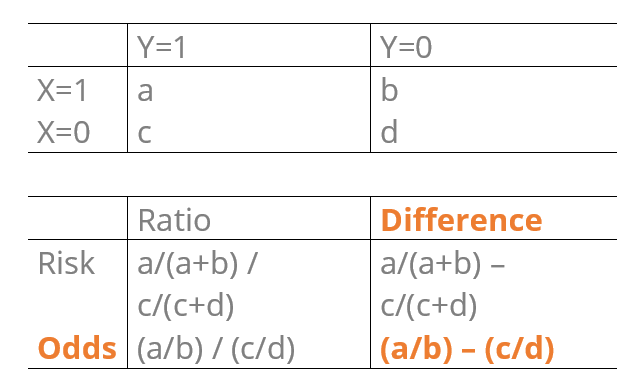



Tim Morris Hate Odds Ratios Hate Risk Ratios Hate Risk Differences Well I M Feeling Cantakerous This Morning And Have Your Back Introducing The Odds Difference Unless You Just Hate Everything




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
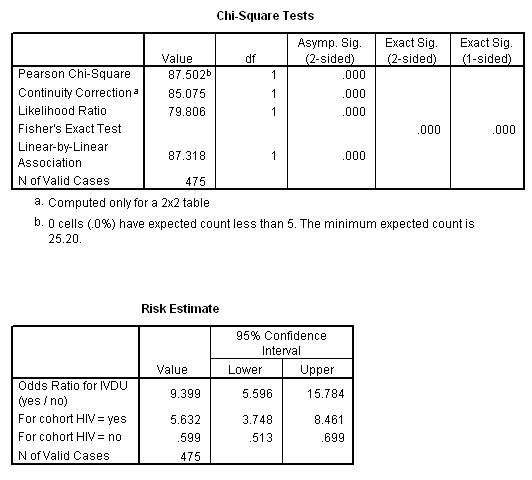



Marg Innovera




Relation Between Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio For Different Values Of Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Image Result For Difference Between Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Cross Sectional Study Hazard Ratio




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




Bar Graph Represents The Summary Odds Ratios Or Relative Risks Of The Download Scientific Diagram
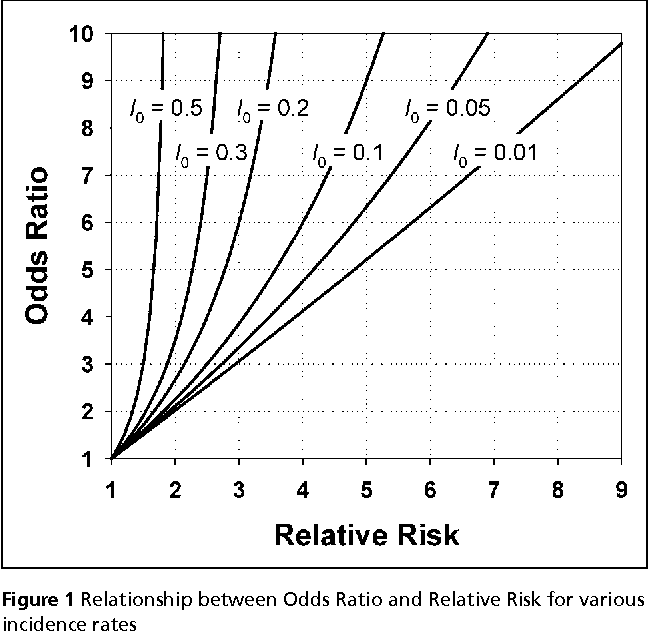



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Absolute Relative And Attributable Risks Outcomes Or Differences That We Are Interested In Differences In Means Or Proportions Odds Ratio Or Ppt Download




Community Medicine Psm Odds Ratio Relative Risk Attributable Risk Population Attributable Risk




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers



No comments:
Post a Comment